Education isn’t just about one way or the usual classroom anymore. If you’re a student figuring out what to do next, a professional looking to advance your career, or just someone curious about new hobbies, there’s definitely a course out there for you.
There are so many options out there! How do you figure out which one is the right fit for you?
Let’s jump into the different types of courses out there, looking at everything from degree programs to specialized skill-based learning.
Why Choosing the Right Course Matters
Picture this:
You’re on a road trip. You’ve got a destination in mind, but there are multiple routes to get there. Some are scenic, others are faster, and a few come with tolls.

Picking the right course for your education and career is kind of like choosing the best path to take. Your career goals, how much time you have, and the resources at your disposal all factor into this decision.
Whether you want to master a technical skill, earn a degree, or simply satisfy your curiosity, understanding the types of courses available can save you time, money, and effort.
Let’s dive right into the various types of courses available in the education system!
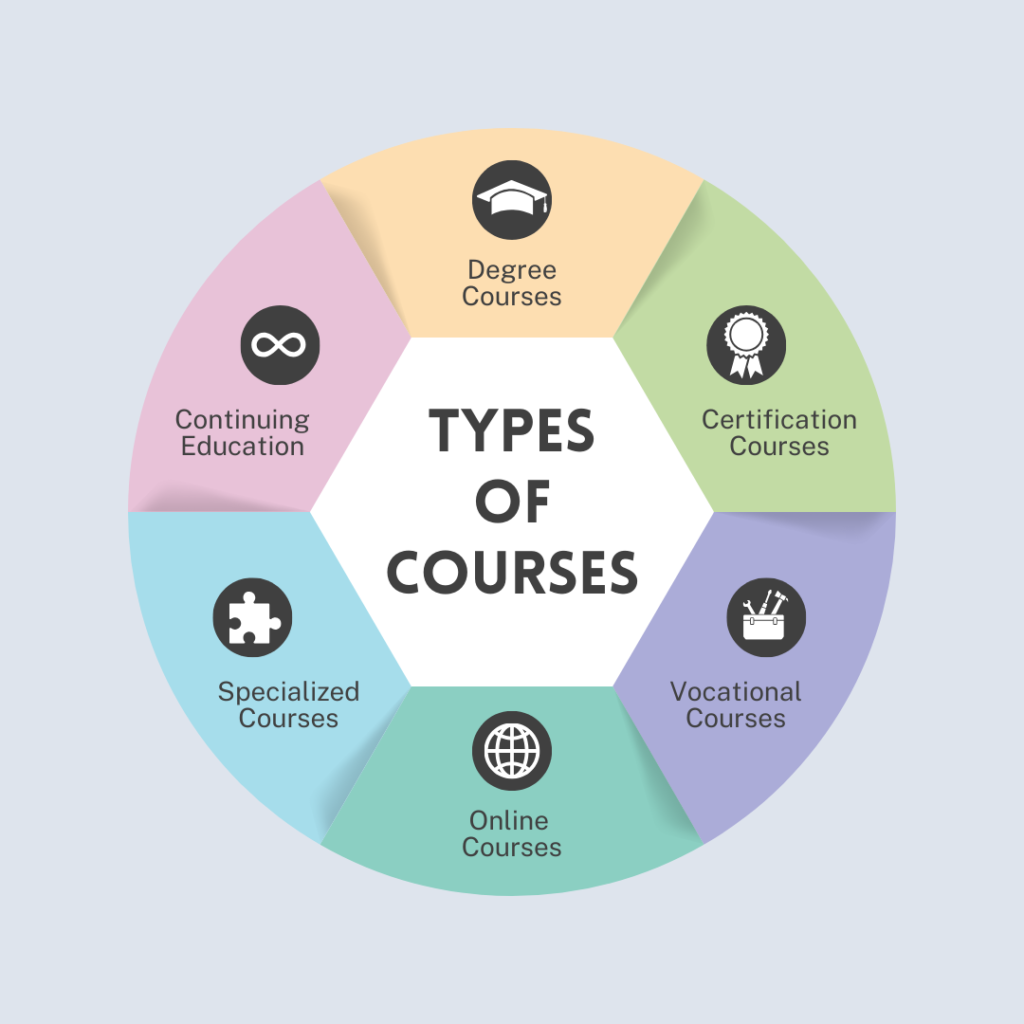
Here is a delightful infographic for you to explore the various options available.
1. Degree Courses
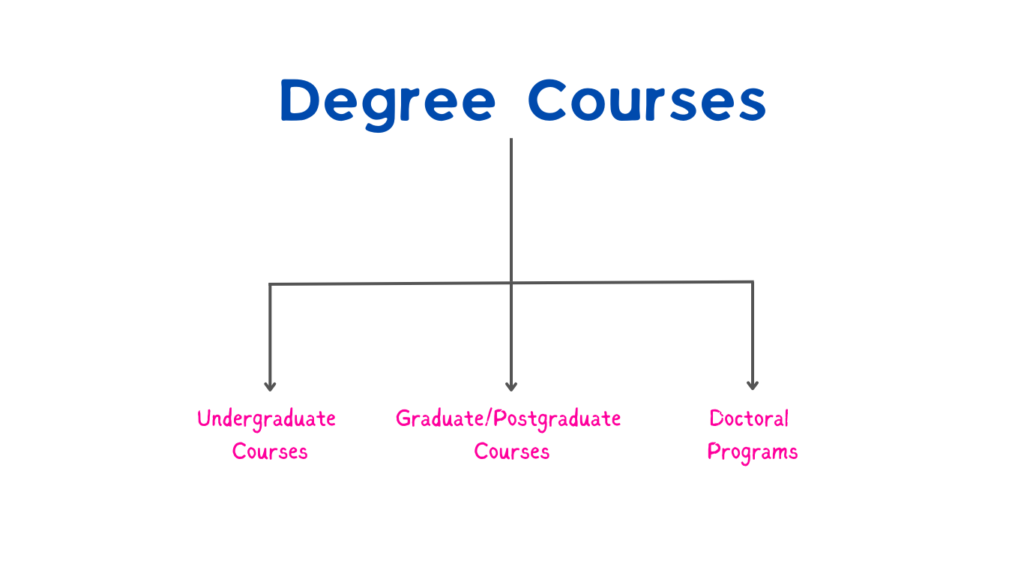
Degree courses are organized programs that universities or colleges offer with the goal of imparting thorough knowledge in a particular field.
These are often prerequisites for certain career paths and are divided into three main levels:
Undergraduate, Graduate/Postgraduate, and Doctoral Programs.
A. Undergraduate Courses
Undergraduate courses are the starting point for higher education, offering a broad foundation in a chosen field of study. These courses are designed to equip students with fundamental knowledge, skills, and practical experience, paving the way for entry-level roles or advanced education.
Key Features:
- Eligibility: Requires completion of high school or equivalent.
- Structure: Mix of core subjects, electives, and hands-on training.
- Duration: Typically 3–4 years, depending on the region and program.
- Outcome: Awards a bachelor’s degree (e.g., BA, BSc, BCom).
Career Opportunities Post-UG Courses
Graduates can explore a variety of opportunities, including:
- Entry-level positions like junior analyst, teacher, or designer.
- Preparing for competitive exams or specialized certifications.
- Continuing education with postgraduate programs for advanced expertise.
B. Graduate/Postgraduate Courses
Postgraduate courses are designed for individuals who wish to deepen their expertise in a specific field or gain advanced professional qualifications. These programs build upon the foundation laid during undergraduate studies and often include research, case studies, and practical applications.
Key Features:
- Eligibility: Requires completion of an undergraduate degree.
- Structure: Focused and specialized curriculum with options for dissertations, projects, or internships.
- Duration: Typically 1–2 years, though some programs like MBAs may include additional requirements.
- Outcome: Awards a master’s degree (e.g., MA, MSc, MBA) or equivalent postgraduate diploma.
Career Opportunities Post-PG Courses
Graduates of PG programs are well-positioned for:
- Mid-level to senior roles in their field (e.g., manager, consultant).
- Academic or research roles, especially in STEM or social sciences.
- Entrepreneurship, utilizing specialized knowledge for business ventures.
C. Doctoral Programs
Doctoral programs, often referred to as PhDs (Doctor of Philosophy), are the pinnacle of academic achievement. These programs focus on advanced research, critical analysis, and original contributions to a specific field of study.
They are ideal for individuals deeply passionate about exploring new ideas, solving complex problems, or pursuing careers in academia and research-intensive industries.
Key Features of Doctoral Programs:
- Eligibility: Typically requires a master’s degree or an exceptional undergraduate record in relevant fields.
- Structure:
- Coursework (in some cases) to build advanced knowledge in the field.
- Independent research under the guidance of a supervisor or mentor.
- Completion of a dissertation or thesis based on original research.
- Duration: Ranges from 3 to 7 years, depending on the subject, research scope, and institution.
- Outcome: Award of a doctoral degree (e.g., PhD, EdD, or professional doctorates in fields like medicine or law).
Career Opportunities Post-Doctoral Programs
Doctoral graduates have access to highly specialized and prestigious roles, including:
- Academia: Professorships, lecturers, and administrative positions in universities and colleges.
- Research and Development: Leading research projects in industries like technology, healthcare, and environmental sciences.
- Specialized Roles: Policy advisors, consultants, or high-ranking positions in governmental and non-governmental organizations.
- Entrepreneurship: Leveraging expertise to create niche businesses or innovative startups.
Level | Examples | Duration | Focus | Career Paths |
Undergraduate | BA, BSc, BCom | 3–4 years | Foundational knowledge | Entry-level jobs |
Graduate/Postgraduate | MA, MSc, MBA | 1–2 years | Specialized knowledge | Mid-level to advanced roles |
Doctoral | PhD | 3–7 years | Research and academic contributions | Professorship, niche industries |
If you want to learn more about the different types of degrees, check out our simple guide that breaks it all down for you.
Certification Courses
Certification courses are designed to help individuals acquire specific skills or knowledge in a particular area. These courses are ideal for career advancement, skill enhancement, or switching to a new professional domain.
Certification programs are typically shorter than degree programs and offer focused training tailored to meet industry demands.
A. Short-Term Professional Certifications
These certifications focus on developing or refining specific skills that are highly valued in today’s job market.
Examples:
- Digital Marketing: Learn SEO, social media management, and analytics.
- Data Analytics: Gain expertise in tools like Excel, SQL, Python, or Power BI.
- Graphic Design: Master tools like Adobe Illustrator, Photoshop, or Canva.
Key Features:
- Duration:
- Typically ranges from a few weeks to a few months.
- Flexible learning formats include weekend or evening classes, ideal for working professionals.
- Flexibility:
- Available both online and in-person, depending on the provider.
- Online certifications often offer self-paced learning to accommodate individual schedules.
Benefits:
- Quick upskilling in high-demand areas.
- Affordable compared to full-time degree programs.
- Credibility and proof of competency in specific skills.
B. Industry-Specific Certifications
These certifications are tailored for specific industries and often serve as benchmarks of expertise.
Examples:
- PMP (Project Management Professional): Recognized globally as a standard for project management.
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect: Validates expertise in designing cloud solutions.
- Azure Administrator Certification: Demonstrates proficiency in Microsoft cloud technologies.
- Six Sigma Certifications: Focus on process improvement and operational efficiency.
Key Features:
- Relevance: Certifications are updated regularly to reflect the latest industry trends and tools.
- Hands-On Training: Many programs include practical assessments or real-world projects to demonstrate skill application.
- Accreditation: Offered by industry-recognized organizations, enhancing their credibility.
Benefits:
- Boosts Career Profiles: Industry certifications are often required for advanced roles and can significantly enhance a resume.
- Increases Earning Potential: Many certified professionals see immediate salary growth.
- Global Recognition: Certifications like AWS or PMP are valued across countries, offering job opportunities worldwide.

Certification courses are a powerful tool for anyone looking to upskill quickly, stay competitive, or pivot into new fields. Whether short-term or industry-specific, these programs provide a fast track to achieving professional success.
Vocational Courses
Vocational courses are job-oriented training programs designed to equip individuals with practical skills and knowledge for specific trades or professions.
Unlike traditional academic programs, these courses focus on hands-on training, making them ideal for those looking to quickly enter the workforce or enhance their employability in specific fields.
Definition and Purpose of Vocational Training
Vocational training provides specialized instruction tailored to the requirements of particular industries. The primary goal is to prepare students for real-world roles by emphasizing practical applications over theoretical knowledge.
Key Features:
- Hands-On Learning: Students engage in activities and simulations that mimic workplace scenarios.
- Industry-Driven Curriculum: Programs are often designed in collaboration with industry experts to meet current job market demands.
- Flexibility: Offered through various formats, including full-time courses, part-time classes, and apprenticeships.
Purpose:
- To bridge the gap between education and employment.
- To empower individuals with skills that align with immediate job requirements.
Examples of Vocational Courses
Vocational courses span a wide range of fields, catering to diverse interests and industries.
- Technical Courses:
- Examples: Automotive repair, welding, electrical installation.
- Prepares students for technical roles in industries like manufacturing and construction.
- Culinary Arts:
- Examples: Baking, professional cooking, food presentation.
- Ideal for aspiring chefs, pastry artists, or food entrepreneurs.
- Healthcare Training:
- Examples: Certified Nursing Assistant (CNA), phlebotomy, medical billing.
- Prepares individuals for healthcare support roles, a rapidly growing sector.
- Creative Trades:
- Examples: Photography, interior design, hairdressing.
- Tailored for those pursuing careers in creative and service-oriented industries.
Focus on Practical Skills and Job-Oriented Outcomes
Practical Skills:
- Vocational courses emphasize real-world applications. For instance, a culinary arts student will spend most of their time cooking rather than studying theory.
- Training often includes internships or on-the-job learning, offering invaluable industry exposure.
Job-Oriented Outcomes:
- Graduates of vocational programs are job-ready, often bypassing the need for extensive additional training.
- Vocational certifications are widely recognized by employers, making them a fast track to employment.
Key Advantages of Vocational Courses
- Quick Entry into Workforce: Most courses are short-term, enabling faster career starts.
- Cost-Effective: Less expensive than traditional degree programs.
- High Employability: Focused training ensures skills directly align with market needs.
- Adaptability: Suitable for individuals of all ages, whether starting a career, transitioning, or upskilling.
Vocational courses are perfect for individuals seeking immediate employment, skill development, or a chance to specialize in a trade. These programs emphasize practicality, making them a cornerstone of workforce development.
Online Courses
Online courses have revolutionized education, making learning more accessible, flexible, and personalized. These courses are offered via digital platforms and cater to a wide range of learners, from students and professionals to hobbyists.
The convenience of learning from anywhere and at any time has fueled the popularity of online education worldwide.
Growth of E-Learning Platforms
E-learning platforms have seen remarkable growth, thanks to advancements in technology and increasing demand for remote education.
Leading Platforms:
- Coursera: Offers courses from top universities like Stanford and Yale, as well as professional certifications.
- Udemy: A vast library of courses on diverse topics, including tech, arts, and business.
- edX: Known for university-level programs, including MicroMasters and professional tracks.
Why the Boom?
- The rise of high-speed internet and mobile devices has made online learning accessible globally.
- A growing focus on upskilling and reskilling has driven individuals and organizations to embrace e-learning.
- Flexibility to learn at one’s own pace appeals to busy professionals and students alike.
Types of Online Courses
Online courses come in various formats, catering to different learning preferences and goals.
- Free Courses:
- Offered by platforms like Khan Academy, LinkedIn Learning (trial), and some university-hosted MOOCs.
- Great for exploring topics without financial commitment.
- Paid Courses:
- Provide comprehensive material and often include certifications.
- Examples include Coursera’s professional certificates, Udemy’s premium courses, and Skillshare memberships.
- Self-Paced Courses:
- Learners progress at their own speed.
- Ideal for individuals with unpredictable schedules or who prefer a relaxed pace.
- Instructor-Led Courses:
- Include live sessions or interactive components like Q&A with experts.
- Mimic traditional classroom settings, fostering a sense of community among participants.
Flexibility, Accessibility, and Credibility of Online Certifications
Flexibility:
- Learn anywhere, anytime, as long as there’s an internet connection.
- Courses are compatible with laptops, tablets, and even smartphones.
Accessibility:
- Affordable alternatives to traditional education.
- Available across diverse subjects, from data science to creative writing.
- Tailored for global learners, often in multiple languages.
Credibility of Certifications:
- Certifications from renowned platforms (e.g., Google, AWS, Coursera) are widely recognized by employers.
- Many online programs partner with universities and companies, boosting their value in the job market.
- Verified certificates often include unique IDs for authenticity.
Key Advantages of Online Courses
- Personalized Learning: Tailored content and pacing to suit individual needs.
- Cost-Effective: Many courses are free or significantly cheaper than traditional programs.
- Global Reach: Access courses taught by experts from leading institutions worldwide.
- Skill Development: Perfect for acquiring new skills or exploring different career paths.
Online courses have democratized education, breaking barriers of location, cost, and time. Whether you’re a student, a professional, or a lifelong learner, online education offers endless possibilities to grow and succeed.
Specialized Courses
Specialized courses cater to individuals seeking expertise in niche areas, allowing them to master unique skill sets that align with their career or personal interests.
These courses focus on targeted knowledge and practical applications in specific fields, offering opportunities for creativity, innovation, and career advancement.
What Are Specialized Courses?
Specialized courses are advanced training programs designed to delve deep into particular topics or skills. Unlike general educational programs, these courses aim to build proficiency in distinct, high-demand areas.
Examples of Specialized Courses
- Creative Fields:
- Graphic Design: Learn software like Adobe Illustrator and Photoshop, branding techniques, and visual storytelling.
- Photography: Explore portrait, landscape, and commercial photography, including post-processing skills.
- Technology and Innovation:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Study machine learning algorithms, neural networks, and AI applications.
- Blockchain Technology: Understand distributed ledgers, smart contracts, and cryptocurrency development.
- Healthcare and Wellness:
- Nutrition Science: Advanced knowledge of dietetics and wellness planning.
- Mental Health Counseling: Techniques in therapy and psychological support.
- Entrepreneurship and Business:
- Startup Incubation: Learn funding strategies, market research, and scaling businesses.
- Luxury Brand Management: Expertise in high-end marketing and brand storytelling.
Opportunities for Creativity or Innovation in Specialized Fields
Creative Freedom:
Specialized courses empower learners to explore unconventional ideas and push boundaries within their fields. For instance:
- A graphic designer might experiment with AR/VR technologies.
- A blockchain developer could create unique applications for social impact.
Innovative Applications:
These courses open doors to innovation, enabling professionals to:
- Develop pioneering AI models for industries like healthcare or finance.
- Design cutting-edge marketing campaigns for niche markets.
Industry Relevance:
Specialized training helps individuals stay ahead of trends, mastering tools and techniques essential for competitive industries like tech, design, or health sciences.
Benefits of Specialized Courses
- Focused Expertise: Offers deep dives into specific topics, ensuring mastery.
- High Employability: Niche skills are often in high demand, leading to lucrative job opportunities.
- Creativity and Growth: Encourages out-of-the-box thinking and innovation.
- Flexibility: Often available in online or hybrid formats, making them accessible globally.
Who Should one opt for Specialized Courses?
Specialized courses are ideal for:
- Professionals: Looking to upskill in emerging technologies or gain a competitive edge.
- Students: Exploring unique career paths or adding niche skills to their resumes.
- Hobbyists: Turning passions like photography or graphic design into careers.
Specialized courses are the key to unlocking potential in highly specific and creative domains. Whether you’re aiming for career growth or personal enrichment, these programs offer the perfect platform to stand out in your chosen field.
Continuing Education and Adult Learning
Continuing education and adult learning courses are designed to meet the evolving needs of professionals and lifelong learners.
These programs focus on upskilling, reskilling, or personal development, offering flexible options for busy individuals.
They cater to those seeking career growth, exploring new interests, or simply staying updated in a rapidly changing world.
What is Continuing Education?
Continuing education refers to courses, workshops, or training programs that help individuals:
- Expand their knowledge and skills.
- Stay relevant in their industries.
- Pursue personal interests or passions.
These courses are ideal for working professionals, returning students, or retirees looking to keep learning alive.
Examples of Continuing Education Programs
- Evening Classes:
- Scheduled after work hours, often in local colleges or community centers.
- Popular subjects: foreign languages, computer skills, and creative writing.
- Weekend Workshops:
- Short-term intensive programs focused on specific skills.
- Examples: Leadership training, public speaking, photography basics.
- Corporate Training Programs:
- Designed for employees, sponsored by employers.
- Common topics include project management, team collaboration, and advanced technical training.
- Online Courses for Adults:
- Flexible options like Coursera, LinkedIn Learning, and Skillshare.
- Subjects range from digital marketing to mindfulness practices.
Benefits for Career Growth
- Upskilling and Reskilling:
- Gain expertise in trending tools or technologies.
- Adapt to new roles or industries with updated knowledge.
- Improved Job Opportunities:
- Continuing education can open doors to promotions or new career paths.
- Certifications and advanced skills often make candidates more competitive.
- Networking Opportunities:
- Evening classes and workshops bring together professionals from diverse industries.
- Participants often build valuable professional relationships.
Benefits for Personal Development
- Confidence Building:
- Learning new skills boosts self-esteem and adaptability.
- Achieving certifications or mastering challenging subjects fosters a sense of accomplishment.
- Exploring Passions:
- Courses allow individuals to dive into hobbies like painting, photography, or creative writing.
- Learning for fun or self-expression can enhance overall happiness and fulfillment.
- Staying Engaged:
- Adult learning keeps the mind sharp and active.
- Opportunities to engage in intellectual discussions or creative pursuits contribute to a vibrant lifestyle.
Who Should Consider Continuing Education?
- Professionals: Seeking career advancement or transitioning into new fields.
- Retirees: Looking to stay active, engaged, and mentally stimulated.
- Lifelong Learners: Anyone passionate about gaining knowledge or exploring new interests.
Flexibility and Accessibility
Continuing education programs are highly flexible, offering:
- Formats: Online, hybrid, or in-person.
- Schedules: Evening or weekend classes to accommodate work or family commitments.
- Affordability: Options range from free online courses to paid certifications or workshops.
Continuing education is an investment in personal growth and professional success, making it a valuable resource for learners at any stage of life.
Conclusion
It’s really important to get a grasp on the different types of courses out there so you can make smart choices about your education and career.
If you’re looking to get a degree, certification, or some specialized training, each of these options comes with its own set of perks that can really help you reach your goals.
If you choose something that matches your interests, time, and resources, you can really open up some great chances for personal growth, skill development, and moving forward in your career.
Education isn’t a one-size-fits-all deal, and checking out these options helps you discover the best path to success for you.
Think about what you really need and pick a course that will help you in your future goals.