If you’re reading this, chances are you’re trying to figure out which degree is the best fit for you.
Whether you’re just starting your journey or considering your next step, understanding the different types of degrees is crucial.
Each one opens doors to various career paths, opportunities, and areas of expertise.
From associate degrees that get you into the workforce quickly, to bachelor’s degrees that offer a well-rounded education, and even advanced graduate programs for those wanting to specialize, there’s something for everyone.
As the level of your college degree rises, so does your earning ability. That’s one more reason why it’s important to know about the different kinds of degrees.
In this guide, we’ll break down the options so you can find the degree that aligns with your goals and sets you up for success.
What is a Degree?
Degrees represent formal recognition of academic achievement and are awarded by accredited educational institutions.
They validate the knowledge and skills acquired through rigorous study and are often a prerequisite for many professional careers.
Benefits of Getting a Degree
Earning a degree can lead to increased job opportunities, higher earning potential, and personal fulfillment.
Additionally, degrees can provide individuals with specialized knowledge and expertise in their chosen field, making them more competitive in the job market.
Obtaining a degree can provide several benefits, including:
- Enhanced job prospects: Many employers require candidates to hold a specific degree.
- Higher earning potential: Statistics show that individuals with higher degrees tend to earn more over their lifetimes compared to those with only high school diplomas.
- Personal development: Pursuing a degree can lead to personal growth, critical thinking, and improved problem-solving skills.
As you navigate your educational options, understanding the various types of degrees available will help you make a choice that aligns with your goals.
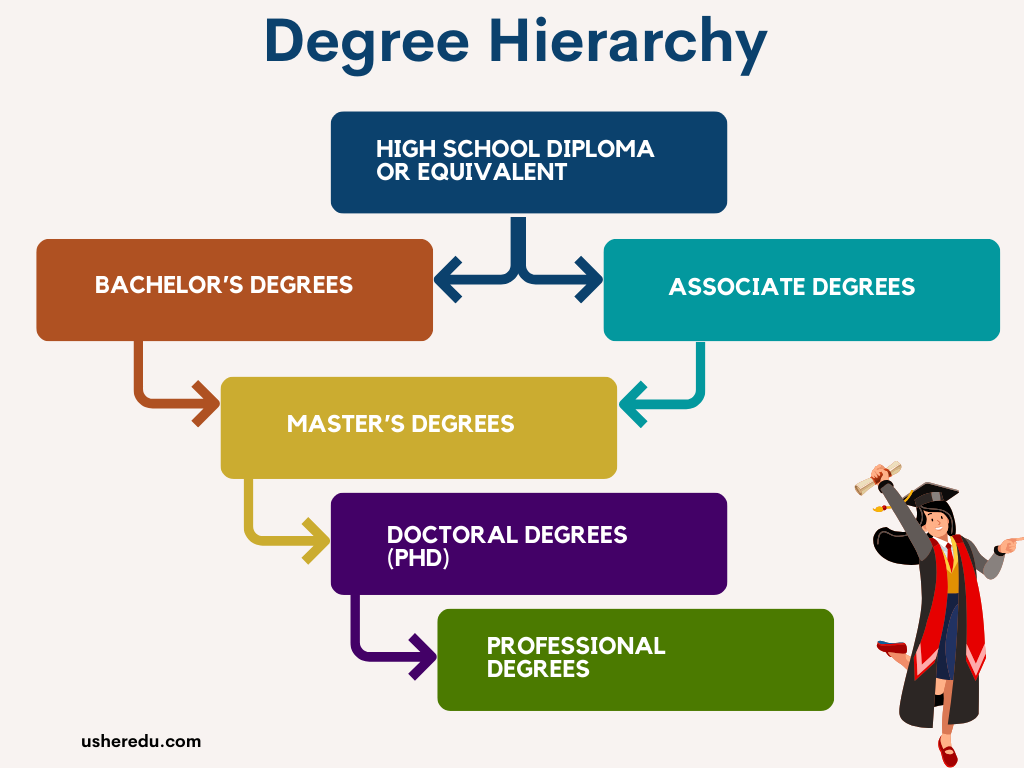
Here’s a clear and organized table showcasing the features of different types of degrees, including the level, duration, purpose, and examples:
Degree Level | Duration | Purpose | Examples |
Associate Degree | 2 years | Basic academic or technical skills; entry into the workforce or step to bachelor’s. | Associate of Arts (AA), Associate of Science (AS), Associate of Applied Science (AAS) |
Bachelor’s Degree | 4 years | Comprehensive education in a specific field; prepares for professional careers or further study. | Bachelor of Arts (BA), Bachelor of Science (BSc), Bachelor of Fine Arts (BFA) |
Master’s Degree | 1–3 years beyond bachelor’s | Advanced knowledge and specialization in a specific field; needed for career advancement or academia. | Master of Arts (MA), Master of Science (MSc), Master of Business Administration (MBA), Master of Education (MEd) |
Doctoral Degree (PhD) | 4–7 years beyond master’s | Highest academic qualification; focus on original research and academic or professional expertise. | Doctor of Philosophy (PhD), Doctor of Education (EdD), Doctor of Business Administration (DBA) |
Professional Degree | Varies (3–7 years) | Required for specific careers, with a focus on practical application in professions like law, medicine, and dentistry. | Juris Doctor (JD), Doctor of Medicine (MD), Doctor of Dental Surgery (DDS |
Types of Undergraduate Degrees
Undergraduate degrees are the foundation of higher education and typically represent the first step toward academic and career advancement.
They are generally categorized into two main types: associate degrees and bachelor’s degrees.
Associate Degrees
Associate degrees are typically awarded by community colleges and vocational schools.
They generally require two years of study, making them a quicker option for individuals looking to enter the workforce or transfer to a four-year institution.
Types of Associate Degrees
- Associate of Arts (AA): Focuses on liberal arts and general education. It prepares students for further study in fields such as humanities, social sciences, and education.
- Associate of Science (AS): Emphasizes mathematics and science courses. Students who want to continue their education in fields like engineering, biology, or healthcare frequently pursue this degree.
- Associate of Applied Science (AAS): Designed for students who wish to enter the workforce directly after graduation, AAS programs focus on technical and vocational skills in fields such as nursing, information technology, and automotive repair.
- Associate of Arts (AA): Focuses on liberal arts and general education. It prepares students for further study in fields such as humanities, social sciences, and education.
Benefits of Associate Degrees
- Cost-effective: They typically cost less than bachelor’s degrees, making them an attractive option for students seeking affordable education.
- Flexibility: Many community colleges offer evening and weekend classes to accommodate working students.
- Transferability: Credits earned in an associate degree program can often be transferred to a four-year institution, allowing students to pursue a bachelor’s degree later on.
Bachelor’s Degrees
Bachelor’s degrees are undergraduate programs that usually require four years of study.
They provide a comprehensive education in a specific field and often include general education courses, major-specific courses, and elective classes.
Types of Bachelor’s Degrees
- Bachelor of Arts (BA): Typically focuses on the liberal arts and humanities. Common majors include psychology, sociology, and literature. BA programs often encourage critical thinking and communication skills.
- Bachelor of Science (BSc): Emphasizes scientific and technical fields. Common majors include biology, chemistry, engineering, and computer science. BSc programs often involve more math and science courses.
- Bachelor of Fine Arts (BFA): Designed for students pursuing careers in the arts, this degree focuses on disciplines such as visual arts, theater, and dance.
- Bachelor of Arts (BA): Typically focuses on the liberal arts and humanities. Common majors include psychology, sociology, and literature. BA programs often encourage critical thinking and communication skills.
Benefits of Bachelor’s Degrees
- Comprehensive education: Students gain a well-rounded education that equips them with critical thinking and analytical skills.
- Increased job opportunities: Many employers require a bachelor’s degree for entry-level positions.
- Pathway to advanced degrees: A bachelor’s degree is often a prerequisite for graduate programs, allowing students to pursue further education and specialization.
Also read: Top 7 Time Management Hacks for Students
Types of Graduate Degrees
Graduate degrees are advanced academic degrees that follow the completion of a bachelor’s degree.
They are designed for individuals seeking to deepen their knowledge in a specific field or to specialize in a particular area of study.
Master’s Degrees
A master’s degree typically requires one to three years of study beyond a bachelor’s degree.
These programs offer advanced training in a specific discipline and often involve coursework, research, and a thesis or capstone project.
Types of Master’s Degrees
- Master of Arts (MA): Often focused on humanities and social sciences, an MA program typically includes a thesis or research project. Common fields of study include history, communication, and education.
- Master of Science (MSc): Emphasizes technical and scientific fields, such as biology, chemistry, and engineering. An MSc program often requires students to conduct research and may culminate in a thesis.
- Master of Business Administration (MBA): Designed for aspiring business leaders, an MBA program covers a broad range of business topics, including finance, marketing, and operations management. Many MBA programs offer concentrations in areas like entrepreneurship, human resources, and information technology.
- Master of Arts (MA): Often focused on humanities and social sciences, an MA program typically includes a thesis or research project. Common fields of study include history, communication, and education.
Benefits of Master’s Degrees
- Career advancement: Many professionals pursue master’s degrees to qualify for higher-level positions and increase their earning potential.
- Specialized knowledge: Graduate programs provide in-depth knowledge and expertise in a specific field, making graduates more competitive in the job market.
- Networking opportunities: Master’s programs often connect students with industry professionals and peers, fostering valuable relationships.
Doctoral Degrees
Doctoral degrees represent the highest level of academic achievement and typically require several years of study beyond a master’s degree.
These programs focus on original research and the development of advanced knowledge in a specific discipline.
Types of Doctoral Degrees
- Doctor of Philosophy (PhD): A research-intensive degree that requires students to complete a dissertation based on original research. PhD programs are offered in a wide range of fields, including the sciences, humanities, and social sciences.
- Doctor of Education (EdD): Designed for education professionals, an EdD program focuses on the practical application of educational theory and research. Graduates often pursue leadership roles in education, policy, or administration.
- Doctor of Medicine (MD): A professional degree required to practice medicine, MD programs involve rigorous training in medical science and clinical practice.
- Doctor of Philosophy (PhD): A research-intensive degree that requires students to complete a dissertation based on original research. PhD programs are offered in a wide range of fields, including the sciences, humanities, and social sciences.
Benefits of Doctoral Degrees
- Expertise and authority: Earning a doctoral degree establishes individuals as experts in their field, often leading to career advancement and recognition.
- Teaching opportunities: Many PhD graduates pursue academic careers, teaching at universities and conducting research.
- Contribution to knowledge: Doctoral research contributes to the advancement of knowledge in a specific discipline, often resulting in publications and innovations.
Did you know that once you finish a doctoral degree, you get to call yourself a doctor, even if you’re not a medical doctor?
How cool is that?
This title represents the pinnacle of academic success and mastery in your selected area of study!
Professional Degrees
Professional degrees are designed to prepare students for specific careers in fields such as law, medicine, and engineering.
These programs typically include both theoretical coursework and practical training.
Examples of Professional Degrees
- Juris Doctor (JD): Required to practice law, a JD program typically takes three years to complete and includes coursework in legal theory, ethics, and practical skills.
- Bachelor of Nursing (BN): This degree prepares students for a career in nursing and often leads to eligibility for licensure as a registered nurse (RN).
- Master of Social Work (MSW): This degree prepares graduates for careers in social work, providing them with the skills needed to support individuals and communities in need.
- Juris Doctor (JD): Required to practice law, a JD program typically takes three years to complete and includes coursework in legal theory, ethics, and practical skills.
Benefits of Professional Degrees
- Job readiness: Professional degrees provide the specific training and qualifications necessary to enter high-demand fields.
- High earning potential: Many professional careers, such as law and healthcare, offer high salaries and job stability.
- Licensing and certification: Many professional degrees are prerequisites for obtaining licenses or certifications required to practice in specific fields.
Online and Distance Learning Degrees
The advent of technology has revolutionized education, making it possible for students to pursue degrees online or through distance learning.
These programs offer flexibility and convenience, allowing students to balance their education with work and personal commitments.
Types of Online Degrees
- Online Associate Degrees: Community colleges and universities offer online associate degrees in fields such as business, healthcare, and technology.
- Online Bachelor’s Degrees: Many institutions provide fully online bachelor’s degree programs, allowing students to earn their degree without attending in-person classes.
- Online Master’s Degrees: Graduate programs in various fields are increasingly available online, enabling professionals to continue their education while working.
- Online Associate Degrees: Community colleges and universities offer online associate degrees in fields such as business, healthcare, and technology.
Benefits of Online Degrees
- Flexibility: Online degrees allow students to study at their own pace and schedule, making it easier to balance work and family responsibilities.
- Access to diverse programs: Online education opens up opportunities to pursue degrees from institutions around the world, regardless of geographic location.
- Cost-effectiveness: Many online programs are more affordable than traditional in-person degrees, reducing the overall cost of education.
Understanding Major and Minor Degrees
In addition to degree types, students often have the opportunity to choose a “major” and, in some cases, a “minor.”
A major is the primary focus of study, while a minor allows students to explore a secondary area of interest.
- Choosing a Major: Your major should align with your career goals and interests. Common majors include business, psychology, engineering, and communications.
- Selecting a Minor: A minor can complement your major and provide additional skills. For example, a student majoring in business might choose a minor in marketing to enhance their expertise.
Benefits of Majors and Minors
- Specialization: Majors provide in-depth knowledge in a specific field, while minors allow for exploration of other interests, making graduates more versatile.
- Enhanced employability: Employers often value candidates with diverse educational backgrounds, making a combination of major and minor degrees appealing.
Choosing the Right Degree for Your Career Goals
Selecting the right degree is as critical a step as choosing the right college in your educational journey.
Consider the following factors when making your decision:
- Career aspirations: Identify your long-term career goals and choose a degree that aligns with your desired profession.
- Industry requirements: Research the qualifications needed in your desired field, as some careers may require specific degrees or certifications.
- Personal interests: Choose a degree that excites you and aligns with your passions. Studying a subject you enjoy can lead to greater success and fulfillment.
The Importance of Accreditation
When pursuing a degree, it’s crucial to ensure that the institution is accredited.
What is Accreditation?
Accreditation is a process in which a university or program is evaluated by an external agency to ensure that it meets certain standards of quality and rigor.
Accreditation can impact the recognition and value of your degree, as well as your eligibility for financial aid or transfer credits.
It’s important to choose a program that is accredited by a reputable organization to ensure that your education will be recognized and respected in the professional world.
Types of Accreditation
- Regional Accreditation: Generally considered the most prestigious, regional accreditation applies to colleges and universities in specific geographic areas.
- National Accreditation: Often associated with vocational and technical schools, national accreditation may have less recognition than regional accreditation.
- Programmatic Accreditation: Certain programs, such as engineering or nursing, may have specialized accreditation to ensure quality and adherence to industry standards.
- Regional Accreditation: Generally considered the most prestigious, regional accreditation applies to colleges and universities in specific geographic areas.
Benefits of Attending an Accredited Institution
- Transferability of credits: Credits earned at accredited institutions are more likely to be accepted by other accredited schools.
- Eligibility for financial aid: Many forms of financial aid, including federal loans and grants, are only available to students attending accredited institutions.
- Enhanced employability: Graduating from an accredited program can enhance your resume and job prospects, as employers often prefer candidates with degrees from recognized institutions.
Difference between Degree and Diploma
When choosing between a degree and a diploma, it’s important to understand the key differences to make an informed decision about your education and career goals.
Feature | Degree | Diploma |
Duration | 2 to 4 years (undergraduate), longer for advanced degrees | 6 months to 2 years |
Scope | Broad education with a mix of general and specialized courses | Focused on specific skills and technical knowledge |
Institution Type | Universities and colleges | Technical schools, community colleges, vocational institutions |
Career Focus | Prepares for professional or advanced career positions | Prepares for entry-level or technical roles |
Cost | Generally more expensive due to longer duration | More affordable with shorter completion time |
Recognition | Higher recognition, often required for advanced careers | Recognized for specific technical or vocational fields |
Coursework | Mix of theory, general education, and specialization | Hands-on, skill-based, job-focused training |
Advancement Potential | Greater potential for career advancement and higher salaries | Good for quick entry into the workforce, limited upward mobility without further study |
Both options have their value; choosing between them depends on your career goals, time, and financial resources.
Conclusion
Education plays a crucial role in personal and professional development, offering individuals the opportunity to gain knowledge, skills, and credentials that can lead to rewarding careers.
With various types of degrees available, understanding your options is essential for making an informed decision that aligns with your goals.
By exploring the different types of degrees, from associate to doctoral programs, and considering factors such as career aspirations and accreditation, you can embark on a fulfilling educational journey that opens doors to new opportunities and enriches your life.
All the Best!