According to Sapien Labs Center for the Human Brain and Mind
- More than 50% of youth aged 18-24 years are struggling with some type of mental health issue.
- Over 90% of students who encounter academic difficulties report mental health issues as a result.
I know, these reports are alarming!
Mental health issues among students and youth are so common these days that they go unnoticed. It’s as if mental health struggles have become a normal part of the student experience.
Importance of Addressing Mental Health for Students
It is important that we start addressing this issue and provide students with the necessary support and resources to improve their mental well-being.
We need to understand that students cannot thrive academically or personally if their mental health needs are not being addressed.
By addressing mental health issues early on, we can help students succeed academically and lead healthier, more fulfilling lives in the future.
Before moving forward, if you are struggling or you feel that you are having any form of mental health issue, please reach out to this number
What Is Mental Health?
Mental health refers to our emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It affects how we think, feel, and act, as well as how we handle stress, relate to others, and make choices. For students, mental health is a critical factor that influences their academic performance, social relationships, and overall quality of life.
Mental health is more than just the absence of mental illness. It involves maintaining a balance in life, being resilient to stress, and being able to bounce back from adversities.
A student who is mentally healthy is better equipped to cope with the challenges they face, both inside and outside the classroom.

Common Mental Health Issues Among Students
Many students struggle with different types of mental health issues during their academic years, but some of the most common challenges include:
Anxiety Disorders: Feelings of worry or fear that interfere with everyday life. This can manifest as generalized anxiety, social anxiety, or panic attacks.
Depression: Persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a lack of interest in activities. Depression can severely impact a student’s ability to concentrate and complete their schoolwork.
Stress: A common issue for students, particularly during exams or major assignments. Chronic stress can lead to burnout, where students feel emotionally drained and unable to function at their usual level.
Burnout: A prolonged state of emotional, mental, and often physical exhaustion. It often leads to decreased motivation and a decline in academic performance.

Mental Health Symptoms to Watch For in Students
It’s important to recognize the signs of mental health issues in students, so they can seek help early.
Common symptoms include:

What causes Mental Health Issues in Students
Academic Pressure
One of the leading causes of stress and anxiety in students is the immense pressure to perform academically. The need to achieve high grades, meet deadlines, and compete for entrance exams, scholarships, or future career opportunities can take a toll on mental well-being.
Students often feel that their academic success defines their worth, which can result in overwhelming feelings of anxiety. The fear of failure or disappointment can lead to chronic stress, affecting both mental and physical health.
Social Challenges
Peer pressure, bullying, and the need to fit in can contribute significantly to anxiety and depression.
Social media has only intensified these issues, as students are constantly exposed to curated images of success, beauty, and happiness, which can create unrealistic expectations for their own lives.
Bullying, both in person and online (cyberbullying), can severely affect students’ mental health, leading to feelings of isolation, low self-esteem, and in extreme cases, self-harm or suicidal thoughts.
Also read: Impact of Social Media on Students
Financial Concerns
For many students, particularly those in higher education, financial stress is a significant contributor to mental health issues. The cost of tuition, accommodation, textbooks, and living expenses can create an enormous burden, leading students to work multiple jobs while studying. The fear of accumulating debt can add to their stress, making it difficult to focus on academic responsibilities.
Life Transitions
Transitions in life, such as moving away from home for the first time, adjusting to a new academic environment, or navigating the transition from high school to university, can be overwhelming. Many students experience homesickness, loneliness, or uncertainty about their future, which can exacerbate mental health struggles.
Lack of Sleep and Poor Nutrition
Mental health is closely tied to physical health. Students often neglect their well-being due to their busy schedules. Lack of sleep, irregular eating habits, an inadequately balanced diet, and consuming unhealthy food can contribute to feelings of fatigue, irritability, and a decrease in cognitive function, making it harder to cope with academic and social challenges.
Impact of Mental Health on Academic Performance
As we have previously discussed, mental health and academic performance are deeply intertwined. A student’s ability to succeed academically is not only influenced by their intellectual capabilities but also by their emotional, psychological, and social well-being.
When mental health issues arise, they can have profound effects on cognitive functions, motivation, attendance, and academic achievement.
Let us look at how mental health can impact a student’s academic performance.
1) Concentration and Focus
Mental health plays a crucial role in a student’s ability to focus and concentrate on their studies. Anxiety, depression, and other mental health conditions can severely impair cognitive functions, making it difficult to process information, retain knowledge, and think critically.
How Mental Health Affects Cognitive Functions?
- Anxiety: One of the most common mental health issues that affect students is anxiety disorder. When a student experiences persistent worry, intrusive thoughts about potential failure or perceived threats frequently consume their minds.
Being anxious all the time can make it hard to focus in class or when studying. Anxiety triggers the body’s “fight or flight” response, which diverts mental resources away from tasks requiring intense concentration. Because they can’t concentrate, students can find themselves reading the same line over and over again or finding it difficult to finish projects. - Depression: Depression impacts concentration by slowing down cognitive processes. Students experiencing depression often report “brain fog”—a sensation where their mind feels sluggish or unable to function as it usually does.
This can make simple tasks feel overwhelming, and complex assignments may become nearly impossible.
For students who need to absorb large amounts of information, such as during exam preparation, this reduced cognitive capacity can lead to frustration, stress, and ultimately lower academic performance. - ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder): Though ADHD is a separate condition, it often coexists with anxiety or depression, further complicating a student’s ability to concentrate.
Students with ADHD may have difficulty sitting still in class, staying organized, and maintaining focus on long-term projects. Without proper support, these challenges can lead to lower grades and a sense of defeat.
Procrastination and Mental Health
Procrastination is a common coping mechanism for students dealing with mental health issues. When faced with overwhelming tasks or the fear of failure, many students delay starting their work in an attempt to avoid the stress associated with it.
Unfortunately, this creates a cycle of increased anxiety and pressure as deadlines approach, exacerbating mental health problems.
For example, a student with social anxiety might avoid group projects or class presentations, procrastinating until the last minute, which increases the likelihood of performing poorly and reinforcing their fear of failure. Procrastination can also lead to poor time management, causing students to fall behind in their studies, further intensifying feelings of inadequacy and helplessness.
Cognitive Overload and Burnout
When mental health is not prioritized, students can reach a state of cognitive overload, where the demands placed on them exceed their mental capacity.
Physical, emotional, and mental exhaustion are signs of burnout, which results from cognitive overload. Burnout can cause students to lose interest in their studies, withdraw from academic and social activities, and struggle to find motivation.
Once a student reaches this point, their academic performance may plummet as they become incapable of maintaining the same level of focus or productivity as before.
Also read: 27 Simple and Effective Study Techniques
2) Attendance and Participation
Class attendance and participation are often the first areas where the impact of mental health issues becomes visible. For students experiencing mental health challenges, attending classes regularly or engaging in classroom discussions can feel insurmountable.
Social Anxiety and Class Participation
Social anxiety is a crippling mental illness that makes it hard for students to participate in class talks, group projects, or presentations. Students who have social anxiety may feel very scared or awkward when they have to speak in front of other people or work closely with their peers.
This can result in students avoiding classes where participation is required, skipping presentations, or choosing to sit silently during discussions, even when they have valuable contributions to make.
Class participation is often tied to a student’s overall grade, especially in college or university settings. As a result, students with social anxiety may receive lower participation grades or miss out on important learning experiences.
The fear of public speaking or performing in front of others can significantly hinder a student’s ability to fully engage with the academic content, even if they have a deep understanding of the material.
Depression and Absenteeism
Depression often leads to chronic absenteeism, as students struggle to find the energy or motivation to attend classes. Feelings of hopelessness, fatigue, and disinterest in activities once enjoyed can make it difficult for students to get out of bed, let alone attend lectures or complete assignments.
Even when students do attend class, they may be physically present but mentally disconnected.
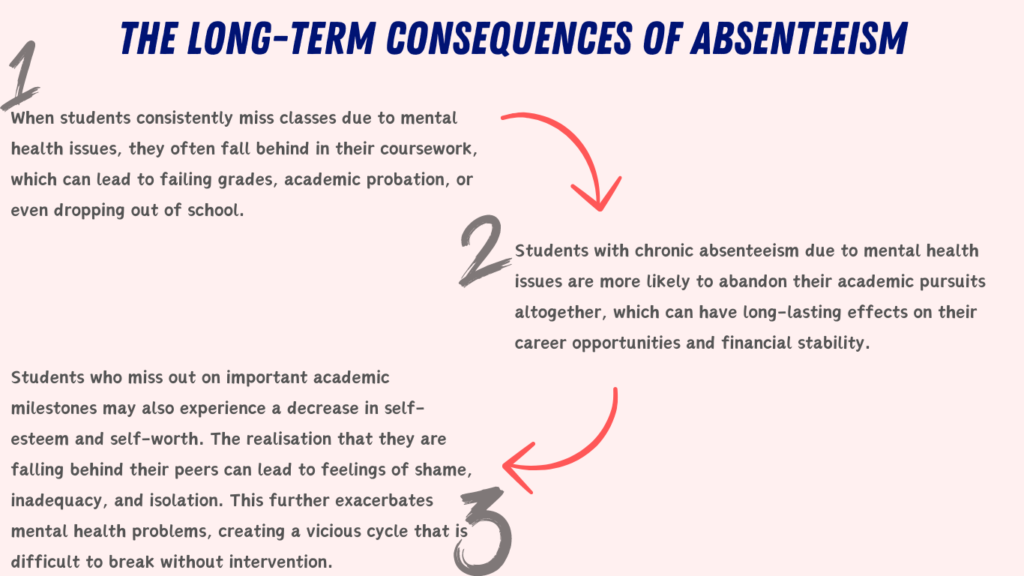
Absenteeism can have a compounding effect on academic performance. Missing class means missing out on important lectures, discussions, and the chance to ask questions or seek clarification.
This creates a knowledge gap that becomes harder to bridge as the semester progresses, leading to more stress, anxiety, and ultimately, a further decline in mental health.
3) Grades and Academic Achievement
Mental health issues can lead to significant fluctuations in a student’s academic performance. While some students may be able to manage their mental health challenges and maintain their grades, others may experience a noticeable decline in their academic achievement as their mental health deteriorates.
Decline in Academic Performance
As students struggle with concentration, absenteeism, and participation due to mental health issues, their grades often begin to suffer.
A student with anxiety may find it difficult to focus during an exam or write an essay, resulting in lower test scores and poor-quality work.
Similarly, a student with depression may lack the motivation to complete assignments, leading to missed deadlines and incomplete projects.
This decline in academic performance can be devastating for students who once excelled in their studies. The realisation that they are no longer achieving the same level of success can lead to feelings of frustration, self-doubt, and hopelessness.
Many students may begin to question their abilities and worth, further intensifying their mental health struggles.
Pressure to Succeed
For many students, the pressure to succeed academically can be overwhelming. This pressure often comes from a combination of external sources—such as parents, teachers, and peers—and internal expectations.
Students may feel that their worth is tied to their academic performance, leading them to push themselves to unhealthy extremes in an attempt to meet these expectations.
This pressure can be particularly intense for high-achieving students who have always excelled academically.
The fear of failure, combined with the weight of expectations, can lead to anxiety, stress, and burnout. These students may also be less likely to seek help, as they feel that admitting they are struggling would be seen as a sign of weakness or failure.
Perfectionism and Its Impact on Mental Health
Perfectionism is another factor that can negatively impact both mental health and academic performance.
Students who set unrealistically high standards for themselves often experience chronic stress, anxiety, and feelings of inadequacy when they fail to meet their own expectations.
Perfectionists may spend an excessive amount of time on assignments, revising and editing repeatedly in an attempt to make their work flawless. This can lead to procrastination, missed deadlines, and frustration when they are unable to achieve the level of perfection they desire.
Over time, perfectionism can lead to burnout, as students exhaust themselves trying to meet unattainable standards. The constant pressure to perform perfectly can take a toll on mental health, leading to anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues that further impact academic performance.
Relationship Between Mental Health and Dropout Rates
Mental health issues are a significant factor contributing to dropout rates in both high school and higher education. Students who struggle with anxiety, depression, or other mental health challenges may find it difficult to keep up with the demands of their coursework, leading them to fall behind.
Over time, the pressure of catching up can feel overwhelming, leading many students to withdraw from school altogether.
According to research, students with untreated mental health issues are twice as likely to drop out of school compared to their peers. The financial, emotional, and social costs of dropping out can be significant, affecting a student’s future career prospects, earning potential, and overall quality of life.
4) Long-Term Consequences on Academic and Professional Life
Mental health affects academic success beyond the classroom. Students with mental health disorders may suffer long-term academic and professional setbacks.
Lower Graduation Rates
As previously indicated, students who do not receive treatment for mental health concerns are more likely to drop out of school.
Even for those who manage to stay in school, mental health challenges can delay graduation. Students may need to take time off to focus on their mental health or repeat courses they failed due to absenteeism or poor performance. This can lead to lower graduation rates and potentially impact their future career opportunities.
Reduced Career Opportunities
The academic performance of a student profoundly influences their future employment opportunities.
When making hiring selections, employers frequently consider a student’s grades, extracurricular activities, and general academic record.
Students experiencing mental health challenges that result in a decrease in their academic performance or hinder their ability to engage in internships, leadership positions, or other activities that enhance their resumes may face a disadvantage in the employment market.
Moreover, the enduring consequences of untreated mental health problems might extend further into the professional environment. Impaired mental well-being can have a negative effect on work productivity, interpersonal connections, and the capacity to manage stress in a professional setting. This may limit career advancement and general job satisfaction.
The Importance of Early Intervention
The good news is that early intervention and proper support can mitigate many of these negative outcomes. Schools, parents, and students themselves can take proactive steps to address mental health issues before they reach a crisis point. By recognizing the signs of mental health challenges and seeking help early, students can develop the coping mechanisms and support systems they need to succeed both academically and professionally.
Effective Coping Strategies for Students
Mental health issues are unavoidable for students, but there are many ways to cope. Learning to manage stress, anxiety, depression, and other mental health disorders is essential for academic performance and well-being.
1) Time Management and Organization
Time management is one of the most critical skills for students to develop, especially when mental health challenges arise.
Poor time management can increase stress and anxiety, as students may feel overwhelmed by their academic workload and struggle to keep up with assignments, deadlines, and exams. By improving time management skills, students can reduce stress, enhance productivity, and create a better balance between academics and personal life.
Also read: Top 7 Time Management Hacks for Students
2) Physical Exercise and Movement
Regular exercise has been shown to reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression, improve mood, and boost overall cognitive function.
For students, incorporating physical activity into their daily routine can be a powerful way to manage stress and enhance academic performance.
3) Mindfulness and Meditation
Mindfulness and meditation are practices that help students develop greater awareness of their thoughts and emotions, leading to improved emotional regulation and reduced stress. Both practices involve focusing on the present moment and accepting one’s thoughts and feelings without judgement, which can significantly impact mental health.
4) Building a Strong Support System
Having a strong network of support is important for mental health, especially when things are difficult. Students who have teachers, friends, and family who are there for them are more likely to be able to handle problems well and feel less alone when they are having mental health problems.
You can utilise the following methods as a support system:
- Talking to a trusted friend or family member can provide emotional relief and help students process their feelings during difficult times.
- Joining a support group with peers who are going through similar experiences helps in offering valuable insights and encouragement.
- Participating in student organisations or clubs that align with your interests is a great way to meet like-minded individuals and build a network of supportive friends.
- Finding mentors who offer direction and counsel can also be very helpful in overcoming obstacles and realising personal development.
- Regular communication with family members, whether through phone calls, video chats, or visits home, can provide a source of comfort and emotional support.
5) Following Sleep Hygiene
Poor sleep hygiene can contribute to mental health problems such as anxiety, depression, and cognitive decline, all of which can negatively impact academic performance.
Developing healthy sleep habits can help students feel more energised, focused, and resilient to stress.
How Does Poor Sleep Affect Mental Health?
Poor sleep can disrupt the balance of chemicals in the brain, leading to mood swings and increased feelings of irritability and the likelihood of experiencing depressive symptoms.
It can impair cognitive function, making it difficult to concentrate and retain information, ultimately affecting overall mental well-being.

6) Maintaining Adequate Nutrition
The connection between diet and mental health is often overlooked, but proper nutrition is essential for maintaining mental well-being. The foods students consume can significantly impact their mood, energy levels, and ability to concentrate.
Impact of Nutrition on Mental Health
- Brain Function: The brain requires a steady supply of nutrients to function properly. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats supports cognitive function and emotional regulation.
- Mood Regulation: Certain foods, such as those rich in omega-3 fatty acids (found in fish, nuts, and seeds) and antioxidants (found in fruits and vegetables), have been shown to improve mood and reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety.
- Energy Levels: Sugary and processed foods can lead to energy crashes and mood swings, whereas a balanced diet with protein, complex carbohydrates, and healthy fats helps maintain stable energy levels throughout the day.
Also read : Why Balanced Diet is Essential for Students
7) Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) Techniques
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a form of psychotherapy that helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors.
CBT techniques can be incredibly effective for managing anxiety, depression, and stress, making them a valuable tool for students struggling with mental health issues.
How does Cognitive Behavioural Theory techniques help students improve their mental health?
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) helps students improve their mental health by making it easier for them to control their emotions, lowering their anxiety and sadness, and teaching them how to solve problems better.
CBT helps students become more aware of their negative thought processes and replace them with healthier, more helpful ones. This makes it easier for them to control their emotions. Students can lessen their anxiety and depression by questioning their irrational views and learning healthy ways to deal with stress.
CBT also teaches useful ways to solve problems, which helps students deal with problems in school and in their personal lives in a more positive and solution-focused way.
8) Seeking Professional Help
Although self-care strategies are essential for managing mental health, there are times when professional help is necessary.
Students should not hesitate to seek support from mental health professionals if they are struggling with anxiety, depression, or other mental health challenges that affect their academic and personal lives.
When should students seek out professional mental health care?
- If a student is experiencing ongoing sadness, hopelessness, or a lack of interest in activities they once enjoyed, it may be time to seek professional help.
- If stress becomes overwhelming and starts to interfere with daily functioning, a therapist or counsellor can help students develop coping mechanisms.
- If a student is having thoughts of suicide, it is critical to seek immediate professional support.
How to Access Mental Health Services for Students?
- Many universities offer free or low-cost counseling services for students. These services are confidential and can provide valuable support.
- Platforms like BetterHelp and Talkspace offer online therapy services that are flexible and accessible for students who may have busy schedules.
- For students in crisis, hotlines such as the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline or text-based services like Crisis Text Line provide immediate support.
- The Government of India has initiated “Manodarpan,” a national helpline for students to access mental health support.
Mental Health Act 2017
The Mental Health Care Act, 2017 is a landmark legislation in India aimed at safeguarding the rights and dignity of individuals with mental illnesses. Its primary goal is to provide comprehensive mental health care services while protecting patients' rights and preventing any form of discrimination.
Key provisions include
Right to Mental Health Care: The Act ensures every person has the right to access affordable and quality mental health services. This includes free treatment for individuals below the poverty line at government facilities.
Decriminalization of Suicide: The Act decriminalizes suicide attempts, recognizing that individuals who attempt suicide are often suffering from severe stress or mental illness, and they should receive care rather than punishment.
Advance Directives: Individuals can make advance directives about their treatment preferences, ensuring their wishes are respected if they become unable to make decisions.
Mental Health Review Boards: Independent boards are established to oversee cases of involuntary treatment and other rights-related issues.
Rights of Persons with Mental Illness: The Act emphasizes the protection of human rights, ensuring no discrimination, abuse, or inhumane treatment, while also promoting community-based care.
The Mental Health Care Act, 2017, represents a significant shift toward patient-centered, rights-based mental health care in India.
Overcoming the Stigma Around Mental Health
Stigma surrounding mental health remains a significant barrier to seeking care, especially among students.
Despite growing awareness of mental health issues, many students still hesitate to seek help due to fear of judgment, discrimination, misunderstanding, or simply because other people are mocking them.
This stigma can prevent individuals from addressing their mental health challenges, which can lead to worsened symptoms, isolation, and a decline in academic and personal well-being.
Overcoming this stigma is essential to creating an environment where students feel safe, supported, and empowered to seek the help they need.
Understanding Mental Health Stigma
Mental health stigma is deeply rooted in historical, cultural, and societal beliefs.
In many societies, mental health issues have long been associated with weakness, moral failings, or even danger.
This has contributed to a culture where mental health problems are seen as something to hide or be ashamed of, leading individuals to avoid seeking treatment.
The pressures placed on students to succeed academically, socially, and personally exacerbate this stigma. They may fear that acknowledging mental health issues will be seen as a sign of weakness or that it could negatively impact their academic and career prospects.
Types of Mental Health Stigma
- Social Stigma: This refers to the negative attitudes and discriminatory behaviors directed at individuals with mental health issues. Social stigma can manifest in many forms, from casual jokes about mental illness to outright exclusion or bullying of those who seek help. This external pressure can make students feel isolated and afraid to share their struggles.
- Self-stigma: It is when people internalize how other people feel about them, which can make them feel ashamed and guilty about their mental health problems. Self-stigma can make people feel bad about themselves and keep them from getting help or realizing how bad their problems are.
- Institutional Stigma: Sometimes, schools, universities, and other institutions inadvertently reinforce stigma through policies, practices, or attitudes that devalue mental health concerns. This might include a lack of mental health resources, an emphasis solely on academic performance, or an environment that discourages vulnerability or emotional openness.
Impact of Stigma on Students
The stigma surrounding mental health has far-reaching effects on students, influencing their academic, emotional, and social well-being.
Students who experience stigma often face barriers to seeking help, which can exacerbate their mental health problems and lead to further complications.
– Delayed Help-Seeking
One of the most significant consequences of stigma is the delay in seeking help. Many students struggle with mental health issues for months or even years before reaching out to a counselor, therapist, or doctor.
This delay can result in worsening symptoms, including more severe anxiety, depression, or other mental health conditions. By the time students seek help, their academic performance, personal relationships, and overall well-being may already be severely impacted.
– Fear of Judgement and Discrimination
Another reason why students might hesitate to ask for help is because they worry about what their peers, teachers, or even potential employers will think of them.
They worry that being labeled as “mentally ill” will result in social exclusion, reduced opportunities for academic or extracurricular involvement, or even discrimination in the job market.
This fear of judgment can be especially strong in competitive academic environments where students feel pressure to appear perfect and capable at all times.
– Internalized Shame and Isolation
For many students, stigma leads to a sense of shame or embarrassment about their mental health struggles.
They may believe that their mental health issues make them “weak” or “inadequate” compared to their peers, causing them to withdraw from social interactions.
This isolation can exacerbate feelings of loneliness and depression, creating a vicious cycle in which students feel increasingly disconnected from those around them.
– Academic Decline and Dropout Rates
When students feel they cannot seek help for their mental health issues, their academic performance often suffers. Untreated mental health issues can have a negative impact on motivation, memory, and concentration, which will result in lower grades and missed deadlines.
In extreme cases, students may feel overwhelmed and consider dropping out of school altogether. By addressing stigma, institutions can help students access the support they need to succeed academically.
Strategies for Overcoming Mental Health Stigma
Overcoming mental health stigma requires a collective effort from students, educational institutions, and society.
There are several strategies that can be employed to challenge negative attitudes, encourage open conversations, and create a supportive environment for mental health.
1. Normalizing Mental Health Conversations
One of the most effective ways to combat stigma is to normalize discussions about mental health. The more people talk openly about mental health issues, the less taboo the subject becomes. Students should feel comfortable discussing their struggles without fear of judgment. This can be achieved through:
- Educational Campaigns: Schools and universities can launch mental health awareness campaigns that focus on educating students about common mental health issues such as anxiety, depression, and stress. These campaigns can help demystify mental illness and emphasize that seeking help is a normal and healthy response to life’s challenges.
- Workshops and Seminars: Offering workshops on mental health and self-care can provide students with valuable tools to manage their well-being while also encouraging open dialogue. Peer-led sessions can be especially effective in creating a sense of community and solidarity.
- Classroom Integration: Mental health education can be integrated into the curriculum, particularly in subjects such as health, psychology, or sociology. Discussing mental health as part of the educational experience helps reduce stigma by presenting it as a legitimate and important aspect of overall health.
2. Promoting Mental Health Role Models
Promoting public figures, athletes, or successful individuals who openly share their experiences with mental health challenges can help students see that mental illness does not define one’s ability to succeed.
These role models demonstrate that it’s possible to live a full, productive life while managing mental health.
By showcasing these individuals, students can feel inspired and encouraged to seek help if they are struggling with their own mental health.
3. Training Faculty and Staff
By providing faculty members with training on mental health awareness and sensitivity, institutions can create an environment where students feel supported and understood.
This training should include:
- Recognizing Warning Signs: Faculty should be trained to recognize signs of mental health struggles in students, such as changes in behavior, attendance issues, or sudden academic decline. Early identification of these signs can lead to timely intervention.
- Responding with Empathy: It is important for faculty to respond to students’ mental health concerns with empathy and understanding, rather than dismissal or judgment. This can encourage students to seek help rather than hiding their struggles.
- Encouraging Access to Resources: Faculty should be knowledgeable about the mental health resources available on campus and be prepared to guide students toward counseling services, support groups, or wellness programs.
4. Offering Anonymous Support Options
For students who still feel uncomfortable seeking help openly, anonymous support options can provide a valuable lifeline.
Many institutions now offer online counselling services, mental health hotlines, or anonymous support groups that allow students to access help without revealing their identity.
These services can be a first step for students who are hesitant to engage with traditional therapy or counselling.
- Online Platforms: Online mental health platforms such as BetterHelp, Talkspace, or campus-specific services can provide students with flexible, anonymous support from licensed professionals.
- Anonymous Peer Support: Some universities have implemented peer support programs where students can connect with trained peers anonymously. These programs provide a space for students to discuss their challenges with someone who understands their experiences.
5. Challenging Stereotypes in the Media
The media plays a significant role in shaping public perceptions of mental health.
Unfortunately, mental health issues are often portrayed in a sensationalized or stigmatized manner, reinforcing harmful stereotypes.
Educational institutions can take a proactive stance by:
- Media Literacy Programs: Offering media literacy programs that help students critically analyze how mental health is portrayed in television, film, and news outlets. These programs can empower students to challenge stereotypes and advocate for more accurate, compassionate depictions of mental health.
- Student-Led Media Campaigns: Encourage students to create their own media projects, such as blogs, podcasts, or videos, that focus on personal mental health stories. This not only gives students a platform to share their experiences but also helps to counteract negative portrayals in mainstream media.
6. Creating Safe Spaces for Mental Health Discussions
Institutions should provide safe, non-judgmental spaces where students can openly discuss their mental health challenges.
Support groups, mental health clubs, and peer counseling programs can offer students a sense of belonging and solidarity.
These spaces should be inclusive, welcoming students from all backgrounds and experiences.
- Support Groups: Establishing mental health support groups on campus, run by trained peers or professionals, enables students to share their experiences in a safe setting. These groups can provide emotional validation, coping strategies, and a sense of community.
- Mental Health Clubs: Student-led mental health clubs can organize events, workshops, and advocacy campaigns that promote mental health awareness and destigmatization. These clubs offer a platform for students to connect with others who are passionate about mental health advocacy.
Long-Term Mental Health Management Strategies for Students
Mental health maintenance isn’t just about dealing with short-term problems; it’s also about creating habits and plans that will help you stay healthy in the long term.
Academic goals, societal responsibilities, and personal growth can cause ongoing stress, anxiety, and depression in students. These issues require both short-term and long-term solutions that build resilience and mental health.
Let us look at some strategies that students can incorporate into their daily lives to manage their mental health in the long term.
Building Emotional Resilience
One of the most important long-term strategies for managing mental health is building emotional resilience. Resilience is the ability to bounce back from adversity, manage stress, and adapt to difficult situations.
For students, resilience can be developed through intentional practice and lifestyle changes.
1. Practicing Self-Compassion
Self-compassion involves treating oneself with kindness and understanding during times of struggle, rather than self-criticism or judgment. Many students place high expectations on themselves and may be overly critical when they fall short. Practicing self-compassion allows students to acknowledge their imperfections and mistakes without feeling overwhelmed by them. This emotional support system helps students bounce back from setbacks and maintain mental well-being over time.
- How to Practice Self-Compassion: Students can start by paying attention to their inner dialogue and actively replacing negative, self-critical thoughts with kind and understanding ones. Mindfulness exercises, such as deep breathing or meditation, can help cultivate self-compassion by encouraging self-awareness without judgment.
2. Cultivating Gratitude
Gratitude is a powerful tool for enhancing emotional resilience and maintaining a positive outlook on life. Research shows that regularly practicing gratitude can improve mood, reduce symptoms of depression, and increase overall well-being. For students, gratitude can serve as a buffer against stress and anxiety by helping them focus on the positive aspects of their lives, even during challenging times.
- How to Practice Gratitude: One simple way to incorporate gratitude into daily life is by keeping a gratitude journal. Each day, students can write down three things they are thankful for, no matter how small. Over time, this practice can shift their focus away from negative experiences and toward a more positive mindset.
Developing Healthy Habits
Developing healthy habits related to sleep, nutrition, and exercise can significantly impact a student’s mental state, providing the foundation for emotional stability and resilience.
1. Prioritizing Sleep
Chronic sleep deprivation is linked to increased levels of stress, anxiety, depression, and impaired cognitive functioning. Students often sacrifice sleep due to academic pressures or social activities, which can have detrimental effects on their mental health over time. Prioritizing sleep as part of a daily routine is essential for long-term mental well-being.
- How to Improve Sleep Habits: Establishing a consistent sleep schedule is one of the most effective ways to improve sleep quality. Students should aim for 7-9 hours of sleep each night, avoid caffeine and electronics before bed, and create a relaxing bedtime routine to signal to the brain that it’s time to sleep.
2. Maintaining a Balanced Diet
Nutrition plays a significant role in mental health. A balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-dense foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, can help stabilize mood, increase energy levels, and improve cognitive function. Conversely, diets high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can contribute to mental health problems, such as anxiety and depression.
- How to Eat for Mental Health: Students should focus on consuming foods that support brain health, such as omega-3 fatty acids (found in fish, nuts, and seeds), antioxidants (found in fruits and vegetables), and complex carbohydrates (found in whole grains). Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water is also important for maintaining focus and energy throughout the day.
3. Regular Physical Activity
Physical exercise is one of the most effective long-term strategies for managing mental health. Exercise releases endorphins, the body’s natural mood boosters, and reduces levels of stress hormones like cortisol. Regular physical activity can help reduce symptoms of anxiety, depression, and stress while also improving sleep quality and boosting self-esteem.
- How to Incorporate Exercise: Students should aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate physical activity most days of the week. This can include activities like walking, cycling, swimming, or participating in sports. Finding an enjoyable form of exercise is key to maintaining it as a long-term habit.
Strengthening Social Connections
The quality of one’s relationships has a significant impact on long-term mental health. Building and maintaining strong social connections can provide emotional support, reduce feelings of loneliness, and increase overall happiness.
1. Building a Supportive Social Network
A strong social support network is crucial for long-term mental health. Friends, family, and mentors can provide emotional support, encouragement, and advice during difficult times. For students, fostering meaningful relationships can help them navigate the ups and downs of academic life and reduce feelings of isolation or loneliness.
- How to Strengthen Social Connections: Students can invest time in building and maintaining close relationships by reaching out to friends, attending social events, or participating in group activities that interest them. It’s also important to seek out positive, supportive individuals who encourage mental well-being rather than contribute to stress or negativity.
2. Practicing Communication and Boundary Setting
Healthy communication is essential for maintaining positive relationships and managing conflict effectively. Students can avoid misunderstandings, improve their relationships, and feel better overall if they learn how to clearly state their needs and feelings.
- How to Practice Effective Communication: Active listening, expressing emotions honestly, and asserting personal boundaries are key components of healthy communication. Students should practice these skills in their relationships, whether with roommates, friends, or family members, to ensure their emotional needs are met and to avoid unnecessary stress.
Promoting Mental Health Awareness and Education
Understanding mental health and knowing when and how to seek help is a critical long-term strategy. Students can benefit from continuous education and self-awareness about mental health issues, enabling them to take proactive steps when needed.
1. Continuous Mental Health Education
Ongoing mental health education helps students become more aware of the signs and symptoms of mental health issues, such as anxiety, depression, and burnout. By staying informed, students can recognize these issues in themselves and others, making it easier to seek help before problems escalate. Educational institutions can play a vital role by providing workshops, seminars, or resources that teach students about mental health and self-care strategies.
- How to Engage in Mental Health Education: Students can take advantage of resources offered by their schools, such as counselling services, mental health seminars, or wellness programs. They can also seek out self-help books, podcasts, or online courses that focus on mental health topics, giving them the tools they need to manage their well-being over the long term.
2. Regularly Seeking Professional Support
Long-term mental health management may sometimes require ongoing support from mental health professionals. Regular therapy or counselling can provide students with a safe space to discuss their challenges, learn coping strategies, and gain insight into their emotional well-being. Even students who are not in immediate crisis can benefit from regular check-ins with a mental health professional to prevent issues from developing into more serious problems.
- How to Access Professional Help: Students can seek therapy or counselling services offered by their school or look for affordable options in their local community or through online platforms like BetterHelp or Talkspace. It’s important to view therapy as a preventative measure, not just something to turn to in times of crisis.
Practising Mindfulness and Stress Management Techniques
Chronic stress is one of the most common mental health challenges students face, and managing it effectively is key to long-term well-being. Mindfulness and stress management techniques can help students stay present, manage anxiety, and prevent stress from accumulating over time.
1. Incorporating Mindfulness Practices
Mindfulness is the practice of being fully present and aware of one’s thoughts, feelings, and environment without judgement. Research has shown that mindfulness can reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression, improve focus, and promote emotional well-being. For students, practicing mindfulness can provide relief from the constant pressures of academic life and help them stay grounded during stressful times.
- How to Practice Mindfulness: Students can start by setting aside a few minutes each day for mindfulness meditation, where they focus on their breath or observe their thoughts without getting caught up in them. Over time, they can incorporate mindfulness into their daily routines, such as by practicing mindful eating, walking, or studying.
2. Using Time Management Techniques
Effective time management is essential for reducing stress and preventing burnout. Many students struggle with procrastination or feel overwhelmed by their academic workload, which can lead to chronic stress. Developing good time management habits can help students balance their responsibilities and maintain a healthier mental state.
- How to Manage Time Effectively: Students can use tools such as to-do lists, planners, or digital apps to organize their tasks and prioritize their work. Breaking larger tasks into smaller, manageable steps can make the workload feel less daunting and reduce procrastination.
Mental Health Helplines and Platforms for Indian Students
To support mental health management, a variety of resources are available, ranging from professional services and helplines to online platforms and government initiatives.
Below is a detailed list of additional mental health resources in India, categorized by type:
1. Government and Institutional Resources
The Indian government has recognized the importance of mental health and has introduced several initiatives and policies to improve access to mental health care and reduce stigma.
National Mental Health Programme (NMHP)
- Overview: The Government of India established the National Mental Health Programme NMHP in 1982 to guarantee the availability and accessibility of mental health care throughout the nation. It aims to integrate mental health care with general health care services and strengthen mental health infrastructure.
- Services: Through this program, mental health services are provided at the district level, and the government has been working to train mental health professionals and improve community-based care.
- Availability: Services are available at government hospitals and through outreach programs in various states.
KIRAN Mental Health Helpline
- Overview: The Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment established KIRAN, a toll-free mental health hotline that offers immediate assistance to those who are in need.
- Services: The helpline operates 24/7 and offers assistance for stress, anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues. The service is available in 13 languages, making it accessible to people from different regions of India.
- Contact: 1800-599-0019
District Mental Health Programme (DMHP)
- Overview: As part of the National Mental Health Programme, the DMHP was introduced to provide mental health services at the district level. It includes training of primary care workers, provision of essential drugs, and public awareness campaigns.
- Services: The DMHP aims to make mental health care more accessible to rural and semi-urban populations, providing early intervention and support.
- Availability: Available in several districts across India, particularly through primary health centers and district hospitals.
2. Helplines and Emergency Services
There are numerous helplines in India that offer free and confidential support to individuals dealing with mental health issues, including students.
iCALL
- Overview: iCALL is a mental health helpline run by the Tata Institute of Social Sciences (TISS) in Mumbai. It offers free, professional counseling services via phone, email, and chat.
- Services: The helpline provides support for issues such as stress, anxiety, depression, relationship problems, and academic pressures. The counselors are trained professionals who offer evidence-based support.
- Availability: Available from 8 AM to 10 PM, Monday to Saturday.
- Contact: 9152987821 or email at icall@tiss.edu
Snehi – Emotional Support and Counseling
- Overview: Snehi is a Delhi-based NGO that offers emotional support and mental health counseling to people in distress, with a particular focus on young people and students.
- Services: Snehi operates a free helpline for those experiencing mental health issues and provides counseling services through trained volunteers.
- Contact: Snehi offers services via phone and online platforms.
The Vandrevala Foundation Mental Health Helpline
- Overview: The Vandrevala Foundation runs a 24/7 mental health helpline to provide immediate support for people experiencing mental health issues. It aims to offer quick, anonymous assistance to anyone in need.
- Services: The foundation provides counseling, crisis intervention, and referrals to mental health professionals. Their services cover a range of issues, including anxiety, depression, and suicidal thoughts.
- Contact: Toll-free number 9999-666-555
3. Online Platforms and Mental Health Apps
The rise of technology has enabled the development of several online platforms and mobile apps that cater specifically to mental health care in India. These platforms provide students with convenient, affordable, and often anonymous access to professional support.
YourDOST
- Overview: YourDOST is an online counseling and emotional wellness platform designed to provide support for students and working professionals. The platform offers access to certified counselors, psychologists, and coaches.
- Services: Users can engage in text-based counseling, audio/video sessions, or chat anonymously with mental health professionals. It covers a wide range of issues including academic stress, career concerns, relationship problems, and anxiety.
- Availability: The platform operates 24/7.
- Website: YourDOST
Wysa
- Overview: Wysa is an AI-driven mental health app that provides users with a “chatbot” to help them manage their mental health. The app offers tools to manage stress, anxiety, and depression through self-care exercises, mindfulness activities, and cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) techniques.
- Services: Wysa provides a mix of AI support and human guidance, offering users daily check-ins, mood tracking, and the option to connect with a trained therapist.
- Availability: Available on Android and iOS.
- Website: Wysa
InnerHour
- Overview: InnerHour is a mental health app created by Indian psychologists, providing evidence-based programs and tools for managing a range of mental health concerns such as anxiety, depression, and sleep problems.
- Services: The app offers self-help programs, personalized activities, and access to qualified therapists for counseling sessions.
- Availability: Available on both Android and iOS.
- Website: InnerHour
MindPeers
- Overview: MindPeers is a mental health platform that offers both digital tools and access to professional counseling. It’s focused on emotional and psychological well-being, with specific support for academic stress and career development.
- Services: The platform provides personalized mental health assessments, therapy sessions, mindfulness exercises, and mental wellness programs designed by professionals.
- Website: MindPeers
4. NGOs and Mental Health Advocacy Organizations
Several non-governmental organizations (NGOs) in India work to raise awareness about mental health issues and provide free or affordable services to those in need.
The Live Love Laugh Foundation
- Overview: Founded by actress Deepika Padukone, the Live Love Laugh Foundation focuses on reducing the stigma around mental health in India. The foundation offers educational resources, campaigns, and mental health services.
- Services: The foundation works on creating awareness about mental health, especially among young people, and offers resources for individuals to seek help. It also provides school-based mental health programs and support for individuals experiencing anxiety and depression.
- Website: The Live Love Laugh Foundation
Manas Foundation
- Overview: Manas Foundation is an NGO based in New Delhi that provides mental health services, particularly to underserved populations. The foundation works on mental health advocacy, awareness, and direct services.
- Services: Manas offers psychological counseling, workshops, and mental health training programs for students and educators. The organization also engages in policy advocacy and public awareness campaigns.
- Website: Manas Foundation
Sangath
- Overview: Sangath is one of India’s leading NGOs working on mental health research and community-based services. It focuses on promoting mental health in youth and adults through innovative, community-based programs.
- Services: Sangath provides counseling services, runs mental health projects in schools, and offers support for families dealing with mental health challenges. It has a particular focus on using low-cost, scalable models to improve mental health care in rural areas.
- Website: Sangath
5. University-Based Counseling Centers and Initiatives
Many universities in India are now recognizing the importance of mental health and are establishing dedicated counseling centers to provide support for their students.
Counseling Centers at Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs)
- Overview: Several IITs across India have established on-campus counseling centers to support students dealing with academic stress, anxiety, depression, and personal issues.
- Services: These centers provide one-on-one counseling, group therapy sessions, and workshops on stress management, time management, and emotional well-being.
- Example: IIT Delhi’s Student Counselling Service offers confidential counseling and conducts wellness programs for students.
National Institute of Mental Health and Neuro-Sciences (NIMHANS)
- Overview: NIMHANS is a premier mental health institution in India that provides clinical services, research, and education in the field of mental health.
- Services: NIMHANS offers a wide range of mental health services, including counseling, psychotherapy, and psychiatric care. Students can access these services either through referrals or as walk-in patients.
- Location: Bangalore
- Website: NIMHANS
6. Peer Support Networks and Community Initiatives
Peer support networks are growing in popularity in India as a way to offer emotional support, mentorship, and community-building among students and young people.
The Mind Clan
- Overview: The Mind Clan is a community-based mental health platform that connects individuals with mental health resources, workshops, and peer support networks.
- Services: The platform offers curated resources, including access to therapists, workshops on mental health topics, and peer support groups. It emphasizes the importance of community in mental health care.
- Website: The Mind Clan
Conclusion
Mental health is an integral part of a student’s academic journey and overall well-being. By understanding the common mental health issues students face, recognizing the signs and symptoms, and utilizing effective coping strategies, students can prioritize their mental health and navigate their academic career with resilience.
It’s important for students to know that they are not alone in their struggles, and seeking help is a sign of strength, not weakness. Schools, teachers, and peers can all significantly contribute to the mental health of students and make sure that no student is left behind by creating an atmosphere of openness and support.